Contents
hide
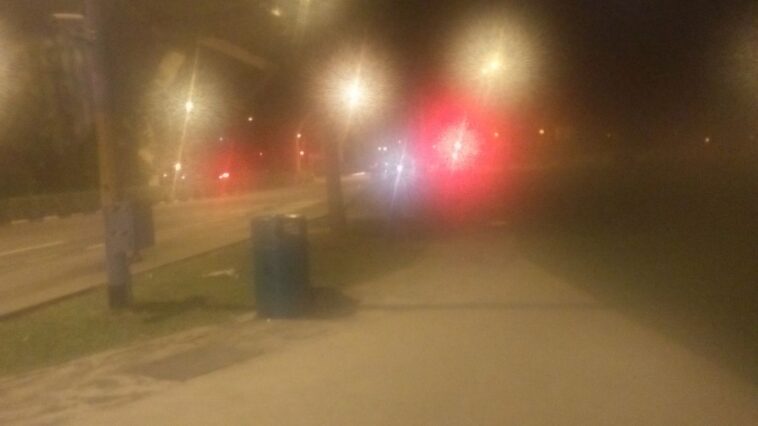
Night driving is often difficult, especially if you have astigmatism. With this condition, headlights and streetlights may look streaky, scattered, doubled or surrounded by halos. These changes can make it harder to read road signs, judge distances, or keep your attention on the road, especially when the lighting is poor or the weather is bad.
Astigmatism is a common vision condition that affects about one in three adults. Many people do not realize that it could be the reason why night driving feels uncomfortable or even unsafe.
In this guide, you will learn why astigmatism changes the way you see lights at night, how it can affect your vision, and what you can do to make night driving safer and more comfortable.
What Is Astigmatism?
Astigmatism happens when the cornea or lens of your eye is not perfectly round.
Instead of being shaped like a basketball, the cornea or lens is more like a football.
Instead of being shaped like a basketball, the cornea or lens is more like a football.
This uneven shape bends light in different directions, so it does not focus properly on the retina. This can lead to several vision problems.
- Blurry vision
- Distorted shapes
- Shadowed or doubled objects
- Light scatter, especially at night
Astigmatism often occurs with:
- Nearsightedness (myopia)
- Farsightedness (hyperopia)
Even a small amount of astigmatism can change the way you see lights at night.
How Astigmatism Affects Vision During the Day
During the day, your pupils are smaller, so less light enters your eyes. This helps reduce the amount of blur you notice.
People with astigmatism may still notice:
- Blurry vision at a distance
- Difficulty focusing
- Eye strain or headaches
- Squinting to see more clearly
At night, these conditions worsen, making vision more difficult.
Why Astigmatism Makes Night Vision More Difficult
In low-light environments, your pupils dilate to let more light into the eye.
This can worsen light scatter, since a larger pupil exposes more of the cornea’s uneven surface.
- The most uneven part of your cornea
- more optical distortion
This is why astigmatism symptoms are often more noticeable at night.
Nighttime Problems From Astigmatism
- Headlights look streaky or stretched.
- Streetlights appear haloed or glowing.
- Lights appear multiplied or doubled.
- Reduced depth perception
- More glare than people without astigmatism
- Harder to see road signs
- Slower reaction time
For many, these symptoms make night driving stressful or unsafe.
Common Light Distortions in Astigmatism
Astigmatism can cause:
1. Halos
Soft glowing circles around lights
(especially on highway lights or headlights)
(especially on highway lights or headlights)
2. Streaks or Lines
Lights appear stretched vertically or horizontally.
3. Starbursts
Lights radiate like a star pattern.
(common when tired or driving at night)
(common when tired or driving at night)
4. Ghosting or Double Lights
A shadow image appears beside the real light source.
5. Scatter / Blur
Hard to tell where the light ends, and darkness begins.
If you notice these symptoms, astigmatism is likely the reason.
Night Driving With Astigmatism: Risks and Safety Tips
Night driving requires:
- fast adjustment to light changes
- strong contrast sensitivity
- accurate depth perception
Astigmatism can affect all of these important parts of your vision.
You may struggle with:
- Judging the distance of oncoming cars
- Seeing lane lines clearly
- Reading reflective road signs
- Seeing pedestrians in low light
- Recovering quickly from headlight glare
Research shows that uncorrected astigmatism can slow your reaction time and make you more sensitive to glare, especially if you are tired or have been driving for a long time.
If night driving feels stressful, you are not imagining it. The way your eyes focus light can truly affect how you see and feel on the road.
How to Improve Night Vision When You Have Astigmatism
The following options can help improve your night vision and reduce problems with scattered light.
1. Updated Toric Glasses
Toric lenses are specially shaped to neutralise the cornea’s irregular curvature.
Benefits:
- Clears up blur
- Reduces light streaks
- Improves contrast
If your glasses prescription is more than a year or two old, your night vision might not be as clear as it could be.
2. Toric Contact Lenses
Contact lenses sit right on your cornea. They help light enter your eye at a better angle.
They can reduce:
- halos
- glare
- distortion
But if your eyes get dry at night, contact lenses might not help as much.
3. RGP / Hard Lenses
Rigid gas-permeable (RGP) lenses create a smooth surface for your eye. They can give you the sharpest night vision.
Great for:
- high astigmatism
- irregular corneas
4. Orthokeratology (Ortho-K)
With Ortho-K, you wear special lenses overnight. They gently reshape your cornea while you sleep.
This lets you wake up with clearer vision during the day, without needing to wear lenses.
This lets you wake up with clearer vision during the day, without needing to wear lenses.
Note:
The results are temporary, so you’ll need to wear the lenses every night to keep your vision clear.
The results are temporary, so you’ll need to wear the lenses every night to keep your vision clear.
5. LASIK or SMILE for Astigmatism
Surgery can reshape your cornea so light focuses the right way.
Benefits:
- High success rate
- Fast recovery
- Reduced glare after healing
Drawback:
You might have some glare or halos for a little while as your eyes heal.
You might have some glare or halos for a little while as your eyes heal.
6. Toric IOLs During Cataract Surgery
If you have cataracts too, a toric intraocular lens can fix both problems at the same time.
This option can help provide a clearer vision for night driving.
Night Driving Glasses for Astigmatism: Do They Work?
You might see ads for yellow-tinted night-driving glasses, but there isn’t much proof that they really work.
They may:
- slightly reduce glare discomfort
- improve contrast for some people
They do not correct astigmatism.
Night-driving glasses might make you feel a little more comfortable, but they don’t actually improve your vision or fix astigmatism.
When to Seek Medical Help for Astigmatism
You should schedule an eye exam if:
- Lights look streaky, doubled, or haloed.
- Night driving feels unsafe.
- You squint or strain to see in the dark.
- Vision worsens in low light.
- Your current glasses don’t work well at night.
Astigmatism can be diagnosed during a routine eye exam. Treating astigmatism can significantly improve your comfort and night vision.
Conclusion
Astigmatism can make lights appear blurry, stretched, haloed, or doubled at night.
These changes can affect how well you judge distance, how quickly you react, and how clearly you see. That can make night driving feel stressful or even dangerous.
The good news? There are ways to improve your night vision.
With the right treatment, such as glasses, contact lenses, Ortho-K, LASIK, or just an updated prescription, most people notice a big improvement in their night vision.
With the right treatment, such as glasses, contact lenses, Ortho-K, LASIK, or just an updated prescription, most people notice a big improvement in their night vision.
If glare or dim lighting at night makes you feel unsafe, talk to your eye doctor. In many cases, a simple fix can help you see clearly again and feel more confident behind the wheel.
FAQ
1. Can astigmatism suddenly get worse at night?
Astigmatism does not change rapidly, but symptoms can feel worse at night because your pupils dilate, allowing more distorted light to enter the eye.
2. Why do I see multiple headlights with astigmatism?
This effect is called ghosting. It is caused by an uneven curvature of the cornea, which causes light to focus at more than one point.
3. Can dehydration or fatigue make night glare worse?
Yes. Dry eyes and tired focusing muscles can increase light scatter caused by astigmatism.
4. Are soft toric lenses or hard lenses better for night glare?
Rigid gas-permeable (RGP) lenses typically provide sharper vision, especially for people with high astigmatism.
5. Does LASIK completely remove halos and starbursts?
In most cases, yes. Once healing is complete, halos and starbursts are usually reduced, although some mild nighttime halos may persist for a short time.