Contents
hide
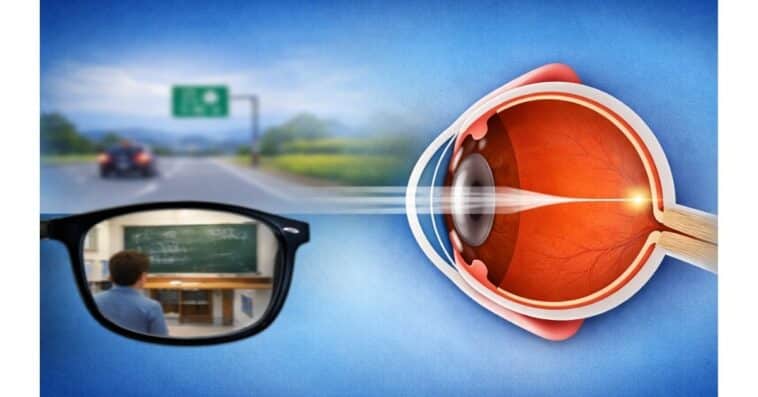
Nearsighted meaning the ability to see nearby objects clearly, while distant objects appear blurry.
Nearsightedness is a common vision problem. If you are nearsighted, you can see things up close clearly, but things that are far away look blurry. The medical term for nearsightedness is myopia. Myopia is one of the most common vision problems worldwide.
If you notice that road signs look blurry, classroom boards are difficult to read, or faces in the distance are not clear, but you have no trouble reading or using your phone up close, you may be experiencing nearsightedness.
Nearsightedness is not considered an eye disease. Instead, it is a focusing problem caused by how the eye refracts light. With proper diagnosis, vision correction, and regular eye exams, most people with nearsightedness can maintain clear, comfortable vision throughout their lives.
What Does Nearsighted Mean?
The definition of nearsightedness is straightforward.
People with nearsightedness see nearby objects clearly, while distant objects appear blurry.
People with nearsightedness see nearby objects clearly, while distant objects appear blurry.
This happens because light entering the eye focuses in front of the retina instead of directly on it. The retina is the light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye that sends visual signals to the brain.
Nearsightedness usually develops when certain changes in the eye affect its ability to focus light.
- The eyeball is slightly longer than normal.
- The cornea is more curved than average.
- Light rays bend too strongly as they enter the eye.
Because of these changes, objects in the distance, such as street signs, whiteboards, or faces across a room, may appear blurred, while tasks that require close-up viewing remain clear.
What Are Nearsighted Eyes?
With nearsightedness, the shape of the eye makes it difficult to see objects that are far away. This condition can become worse over time, especially in children and teenagers while their eyes are still developing.
People with nearsighted eyes often:
- Squint to see distant objects more clearly
- Move closer to screens, books, or signs in order to see them more clearly.
- Notice that their distance vision gradually worsens over months or years
Nearsightedness usually starts in childhood or the teenage years. It often stabilizes in early adulthood, typically after the eyes finish growing.
Symptoms of Nearsightedness
Symptoms of nearsightedness often come on slowly. This can make them hard to notice at first.
Common signs include:
- Blurry vision when looking far away
- Squinting to improve clarity
- Eye strain or visual fatigue
- Headaches after distance viewing
- Trouble seeing signs, boards, or distant screens
Children with nearsightedness may not say they have trouble seeing. They might sit close to the TV or hold books close to their eyes. An eye exam can determine whether nearsightedness is the cause.
Nearsightedness in Children vs Adults
Nearsightedness can look different in children and adults. Here are the main differences.
Feature | Children with Nearsightedness | Adults with Nearsightedness |
| Awareness of symptoms | Often unaware of vision problems | Usually notice blurry distance vision |
| Common signs | Squinting, sitting close to screens, rubbing eyes | Trouble reading road or store signs |
| Impact on daily life | Learning difficulties, trouble seeing classroom boards | Difficulty driving, especially at night |
| Progression | Often progresses as the eyes grow | Usually stabilizes after early adulthood |
| Risk of worsening | Higher during growth years | Lower if vision is stable |
| Night vision | Usually normal | May experience night myopia |
| Detection | Often found through school or routine eye screenings | Diagnosed after noticeable vision changes |
| Importance of exams | Critical for early control and slowing progression | Important for maintaining safe vision |
Causes of Nearsightedness
Nearsightedness is closely related to the way the eye grows and how it focuses light onto the retina.
✔ Genetics
- Myopia often runs in families. This means genetics can play a big role.
- If one or both parents are nearsighted, the risk of nearsightedness in their children is higher.
✔ Eye Shape
- Nearsightedness can happen if the eyeball is longer than normal.
- It can also develop if the cornea, which is the clear front part of the eye, is more curved than normal.
✔ Lifestyle Factors
- Spending a lot of time reading or using screens close up may increase the risk of nearsightedness.
- Children who spend less time outdoors may have a higher risk of nearsightedness.
Spending more time outdoors may help lower the risk of myopia in children.
Risk Factors for Nearsightedness
Several things can raise the risk of nearsightedness, especially in children and teenagers. You may be at higher risk if you:
- Have a family history of myopia, particularly if one or both parents are nearsighted.
- Spend prolonged time on near-vision activities, such as reading, studying, or using digital screens.
- Spend limited time outdoors, which has been linked to higher rates of myopia development.
- Notice vision changes at a young age, as early-onset myopia is more likely to worsen over time.
If these risk factors are identified early, your eye doctor can monitor your vision more closely and suggest ways to slow the progression of myopia.
How Nearsightedness Is Diagnosed
Nearsightedness is usually found during a routine eye exam. The exam is quick and painless. An eye care professional will check how well you see at different distances and look at the health of your eyes.
During the exam, your eye doctor may do several standard tests, including:
- Visual acuity testing, to measure how clearly you can see distant objects
- Refraction testing, to find the lens prescription you need for clear vision
- Eye health evaluation, to check the cornea, retina, and optic nerve
- Dilated eye exam, if needed, to give a better view of the retina and check for other eye problems.
These tests confirm if you have nearsightedness and help rule out other causes of blurry distance vision. Once you have a diagnosis, your eye doctor can recommend the best treatment to restore clear vision and protect your eye health.
Treatment Options for Nearsightedness
✔ Eyeglasses
Eyeglasses are a simple and safe way to correct nearsightedness. They help light focus on the retina so you can see clearly.
✔ Contact Lenses
Contact lenses can give a wider field of view than glasses. There are different types, such as soft lenses, hard lenses, and special lenses for people with astigmatism.
✔ Refractive Surgery
For adults whose vision has stabilized, refractive surgery may reduce or even eliminate the need for glasses or contact lenses.
- LASIK: A laser reshapes the cornea after making a thin flap. Recovery is usually quick with little discomfort. Vision often improves within days.
- PRK: The laser reshapes the cornea without making a flap. This is often recommended for people with thinner corneas. Healing takes a bit longer.
- LASEK: This is similar to PRK but keeps more of the cornea’s surface layer. It is sometimes used when LASIK is not suitable.
- SMILE: This is a newer, minimally invasive laser procedure that uses a very small cut. It may lower the risk of dry eye symptoms.
Not everyone is a candidate for refractive surgery, and a full eye evaluation is required.
Slowing Myopia Progression in Children
In children, nearsightedness may get worse as the eyes grow. Early treatment can help slow it down.
Options that may help include:
- Low-dose atropine eye drops can slow eye growth and reduce myopia progression.
- Increased outdoor time has been linked to a lower risk of worsening myopia.
- Orthokeratology (overnight lenses), which gently reshape the cornea while a child sleeps
- Dual-focus or multifocal contact lenses may help reduce eye strain and slow the progression of myopia.
Early diagnosis, regular eye exams, and follow-up are important for protecting your child’s long-term vision.
Living With Nearsightedness
With the right care, most people with nearsightedness can keep their vision clear and protect their eyes.
Helpful habits include:
- Scheduling regular eye exams to monitor vision changes
- Using good lighting for reading and close-up tasks
- Take regular breaks from screens by following the 20-20-20 rule to help reduce eye strain.
- Wearing prescribed glasses or contact lenses consistently
- Protecting your eyes during sports or hazardous work
- Avoiding smoking, which increases the risk of eye disease
Managing nearsightedness means keeping your vision clear now and protecting your eye health for the future.
When Should You See an Eye Doctor?
If you notice changes in your vision that make it hard to work, study, or drive, it is important to schedule an eye exam. Finding nearsightedness early can help you see better and lower the risk of future vision problems.
You should see an eye doctor if you experience:
- Persistent blurry distance vision, such as difficulty seeing road signs or classroom boards
- Frequent headaches or eye strain, especially after prolonged visual tasks
- Difficulty driving, particularly at night or in low-light conditions
- Vision concerns reported by a teacher, including trouble seeing the board or following lessons
See your eye doctor Immediately If You Notice:
- Sudden flashes of light
- A rapid increase in floaters
- A dark curtain or shadow moving across part of your vision
These symptoms can be warning signs of retinal detachment, a serious eye emergency that requires immediate treatment. People with high or severe nearsightedness are at higher risk and should get medical care right away if these symptoms occur.
FAQ
What does nearsighted mean in simple terms?
It means you see nearby objects clearly, but distant objects appear blurry.
It means you see nearby objects clearly, but distant objects appear blurry.
Is nearsightedness the same as myopia?
Yes. Myopia is the medical term for nearsightedness.
Yes. Myopia is the medical term for nearsightedness.
Can nearsightedness be cured?
There is currently no permanent cure for nearsightedness, but vision can usually be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
There is currently no permanent cure for nearsightedness, but vision can usually be corrected with glasses, contact lenses, or refractive surgery.
Does nearsightedness get worse over time?
Nearsightedness often gets worse during childhood, but it usually stabilizes in adulthood once the eyes have finished growing.
Nearsightedness often gets worse during childhood, but it usually stabilizes in adulthood once the eyes have finished growing.
Final Thoughts
Understanding what nearsightedness is can help you recognize early changes in your vision and take steps to address them. Nearsightedness is a common condition that is manageable and highly treatable with the right care.
If you or your child has difficulty seeing objects in the distance, scheduling an eye exam is the first step toward clear, healthy vision.